Types of Periodontal Disease
Types of Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease is a term that refers to two types of gum disease: gingivitis and periodontitis. Both types of periodontal disease are caused by an infection of bacteria in the periodontal tissues, but each differs in the extent of damage caused to the affected tissues.
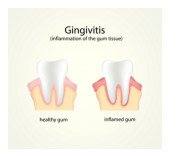
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the least severe type of periodontal disease and also the most common. Gingivitis is relatively mild, and may cause little or no symptoms in its earliest stages. However, as it progresses, it can cause inflammation of the gums, and they may bleed easily when brushed or flossed. Typically, poor oral hygiene and brushing habits are to blame for gingivitis, although other risk factors, such as systemic disease and smoking, can increase the likelihood of developing the disease.
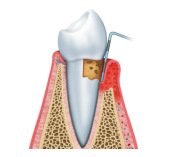
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a much more severe form of periodontal disease that occurs when gingivitis is left untreated and the body is incapable of fighting oral tissue infections on its own. Patients with periodontitis begin to experience a receding of the gum line, and bones that support the teeth may begin to erode as well. Over time, this leads to a loosening of the teeth, and the gums may begin to pull away from the teeth allowing for more bacteria to proliferate beneath the gum line.
The most common type of periodontitis is known as chronic periodontitis, which causes constant inflammation in the tissues supporting the teeth. This type of periodontitis is characterized by a slow progression, during which pockets form between the gums and teeth. Other types of periodontitis include aggressive periodontitis, necrotizing periodontal disease and periodontitis as a manifestation of systemic diseases.
The most common type of periodontitis is known as chronic periodontitis, which causes constant inflammation in the tissues supporting the teeth. This type of periodontitis is characterized by a slow progression, during which pockets form between the gums and teeth. Other types of periodontitis include aggressive periodontitis, necrotizing periodontal disease and periodontitis as a manifestation of systemic diseases.
Copyright © 2022 Advanced Dentistry Northwest. All Rights Reserved