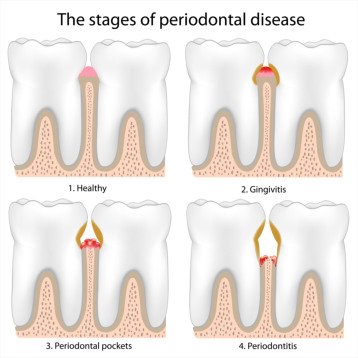
Periodontal disease, or gum disease, is an infection/inflammation of the gum tissues. It is a persistent bacterial infection around the gums and the bone that supports your teeth. Periodontal disease begins as a silent disease that often causes no initial pain or uncomfortable symptoms, but instead slowly causes a deterioration of the supporting tissues in the mouth. Bacteria that are not properly removed from the teeth begin to proliferate, turning into a hardened build-up of plaque on the teeth.
If the irritants (plaque, tartar, debris, etc) are not removed mechanically, the body's immune response will continue to create inflammation trying to remove the irritants. The initial inflammatory respsonse from the gums is called gingivitis. However, if the gingivitis is not reversed, untreated gingivitis can worsen, and the gums may even begin to detach from the teeth. The chronic inflammation of the gums promotes the break down of the jaw bone, and this condition is known as periodontitis. It can result in a loss of teeth and increased risk of other health complications, such as heart attack or stroke. It is estimated that about 47.2% of adults in the U.S. suffer from gum disease - according to American Academy of Periodontology.
Daily oral hygienic habits, such as brushing and flossing, are primary factors in determining whether someone is at risk for developing gum disease. Other major factors include nicotine use, uncontrolled diebetes, and the patient's bad occlusion. Genetics do also play a big role. Routine dental care – including frequent professional dental cleanings – goes a long way in preventing periodontal disease.